Strength of materials questions.
Find Strength of materials university examination questions in acaproso.com
| # | Question |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Mathematical Calculation |
| 2 |
Mathematical Calculation |
| 3 |
Mathematical Calculation |
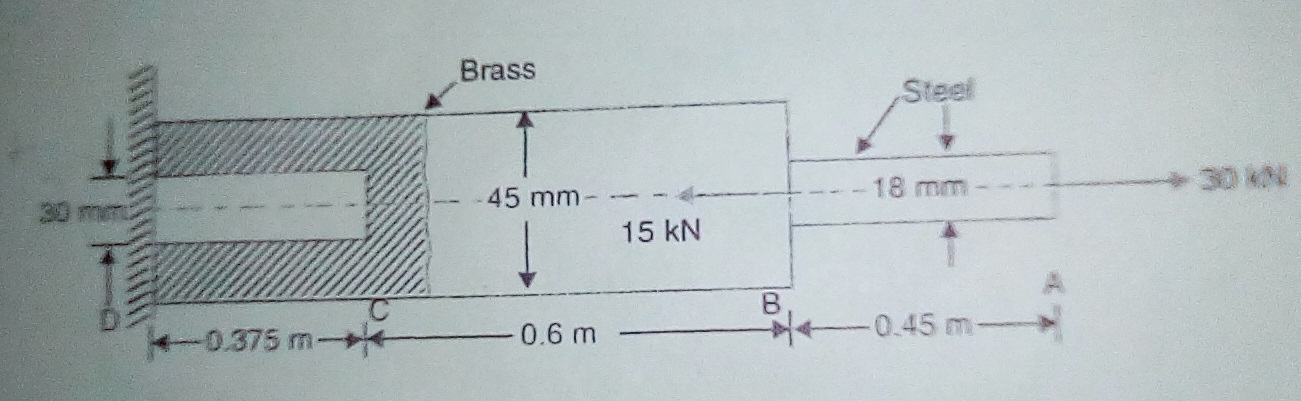
| 4 | An axially loaded bar made of brass and steel has dimensions as shown in the figure below.
Two axial forces P1 and P2 are acting in the direction shown at points A and B respectively with P1=30 kN and P2= 15kN. The Modulus of Elasticity for steel and brass are given as 210 and 105 GPa respectively. Calculate
Mathematical Calculation |
| 5 |
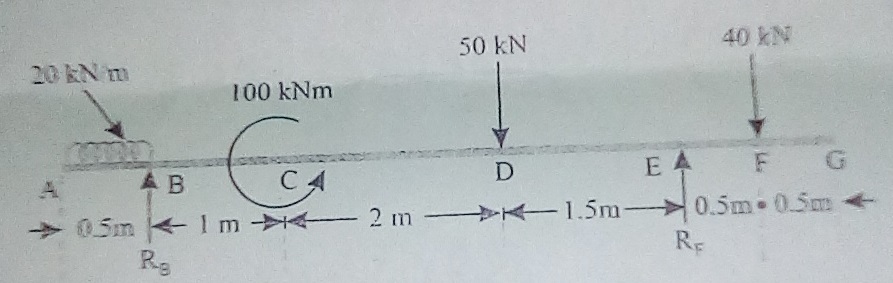
Calculate the reactions and forces acting at different points on the beam and draw the shearing force and bending moment diagrams.
Mathematical Calculation |
| 6 | A rectangular beam with cross sectional dimensions of 250mm (depth) and 150mm (width) is subjected to a maximum bending moment of 750kNm. UNder such loading determine
Mathematical Calculation |
| 7 | A simply supported beam BCDF has the following dimensions: BC=15m, CD=15m, DF=30m. The beam carries a concetrated load of magnitude 200kN at point C and another one of magnitude 80kN at point D. In addition, there is a uniformly distributed load (UDL) of magnitude 10kN/m over the 30m length DF. The beam is simply supported at the point B and F and has a uniform cross section. Draw the shearing force and moment diagrams for this loading of the beam. Short answers |
| 8 | A horizontal beam of uniform cross sectional area is 6m long and is simply supported at its ends. Two vertical concentrated loads of magnitude 48kN and 40kN act at distances 1m and 3m respectively from the left end support. Given that E=200GPa and I=85x10-6m4, determine the position and magnitude of the maximum deflection. Mathematical Calculation |
| 9 |
Mathematical Calculation |